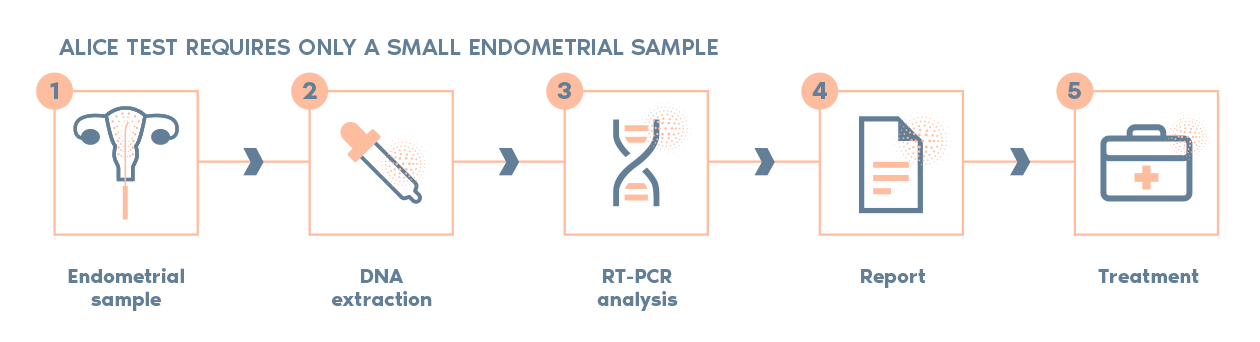
SAT Sperm Aneuploidy Test
Analysis of sperm chromosomal abnormalities.
2,000 spermatozoon analyzed for each chromosome.
2 independent evaluators work in every case.

Results compared with internal control to assure highest reliability.

In case of positive result, we will provide personalised guidance
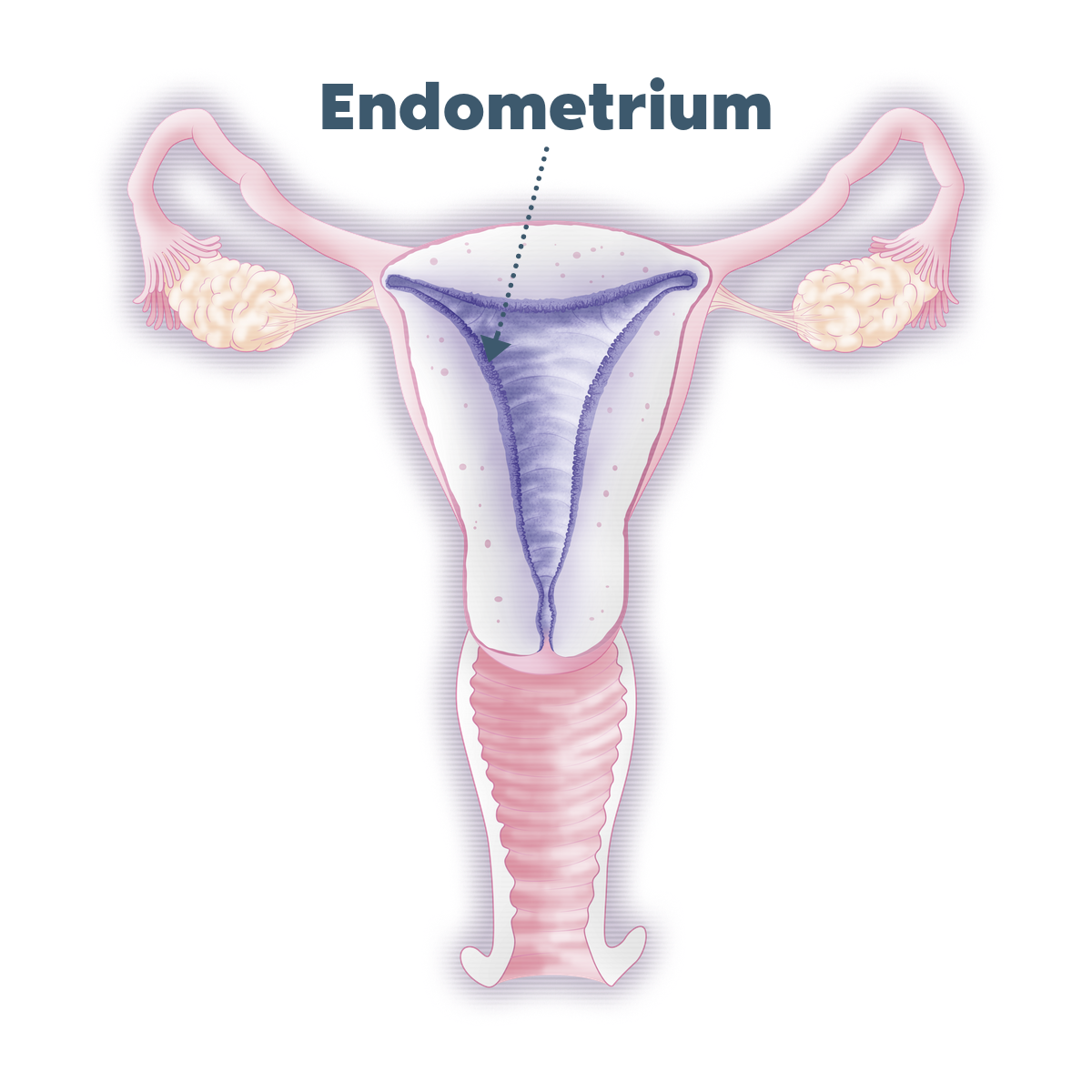
What is SAT?
> SAT is a test to study the genetic factor of male infertility.
> This test evaluates the percentage of spermatozoa with chromosomal abnormalities in a sperm sample.
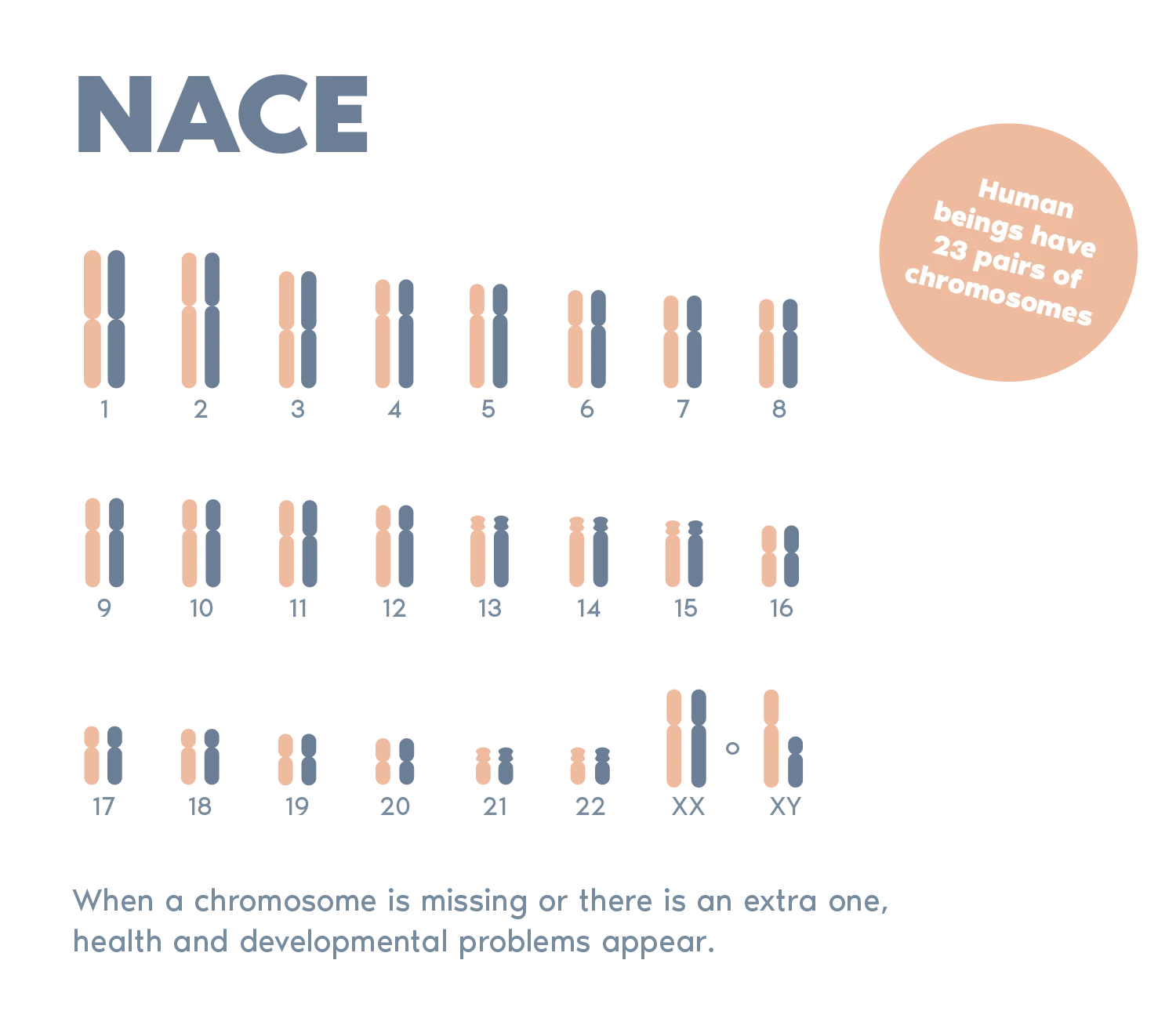
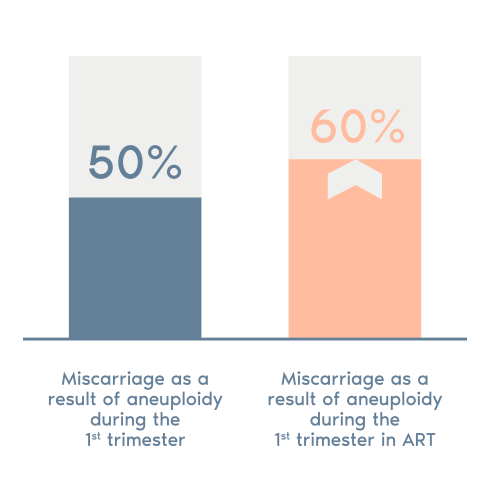
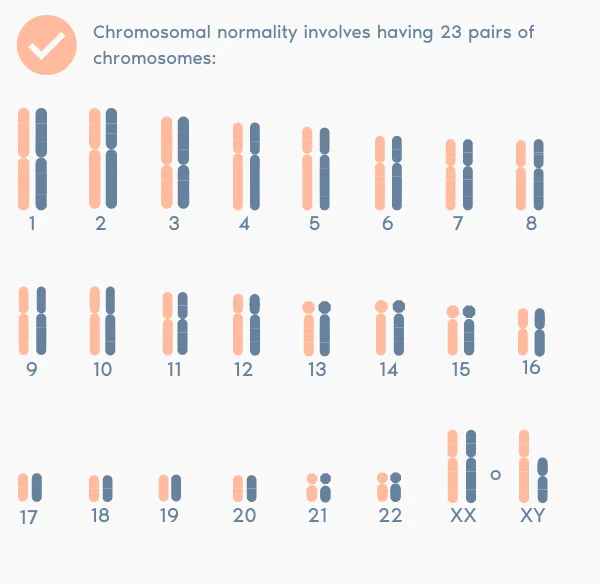
> Analysis is performed on the chromosomes most frequently associated with spontaneous miscarriages and children with chromosomal abnormalities (chromosomes 13, 18, 21, X and Y).
Why use SAT?
> Increases pregnancy rate.
> Decreases miscarriage risk.
> SAT helps to provide personalised genetic guidance to the couple before IVF treatment
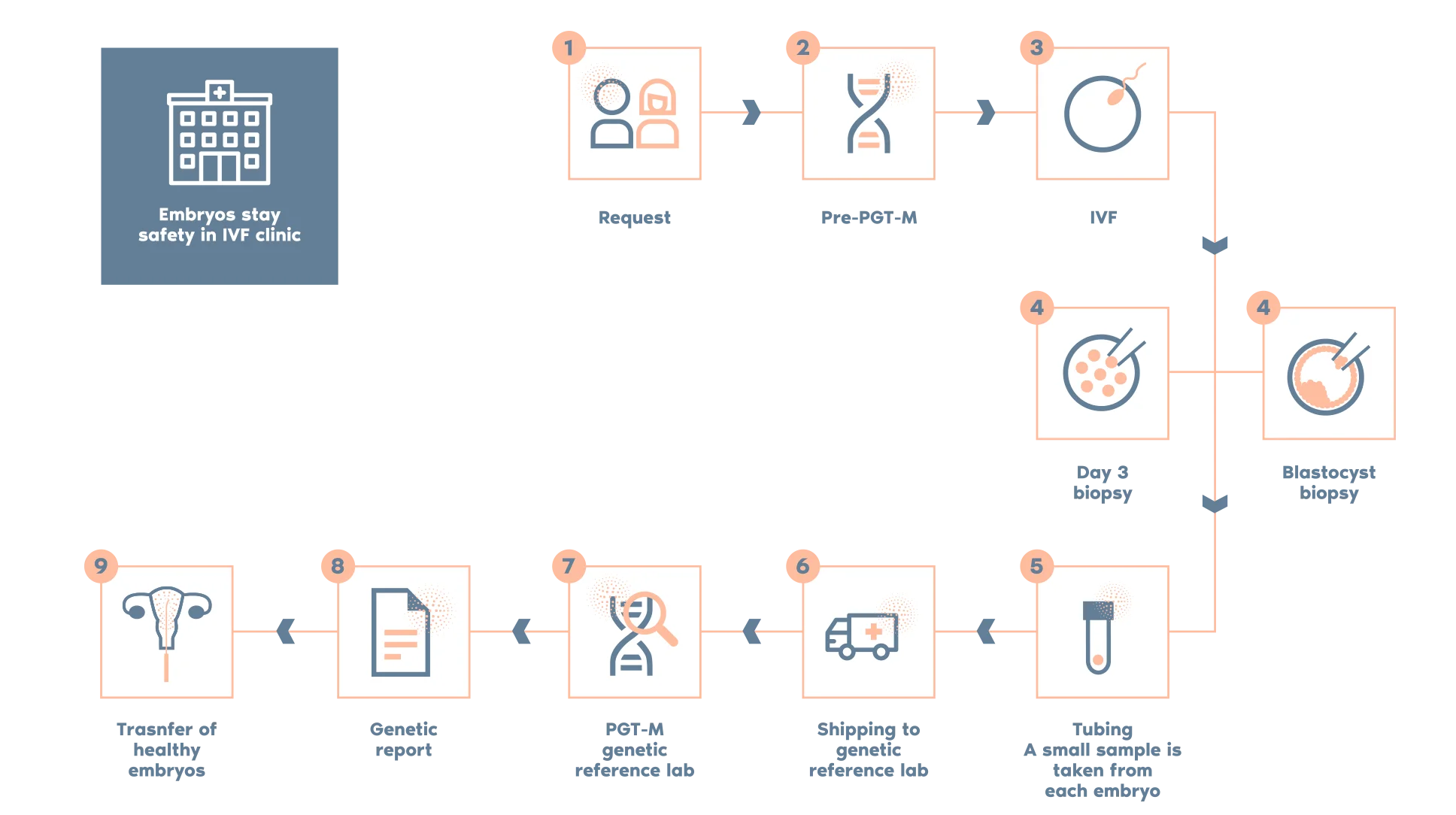
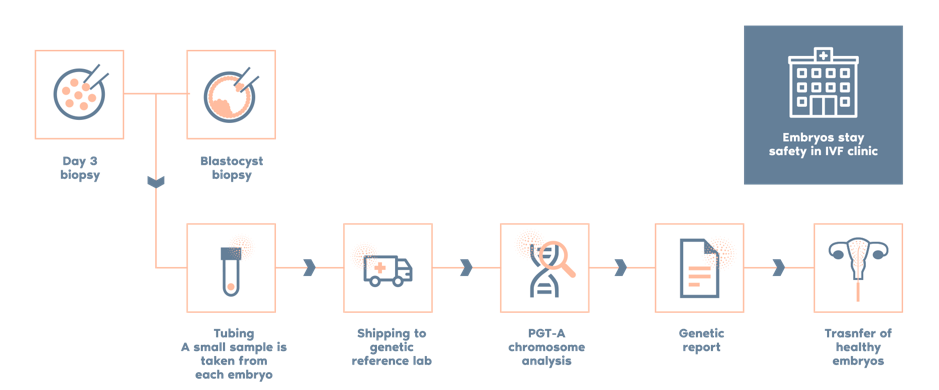
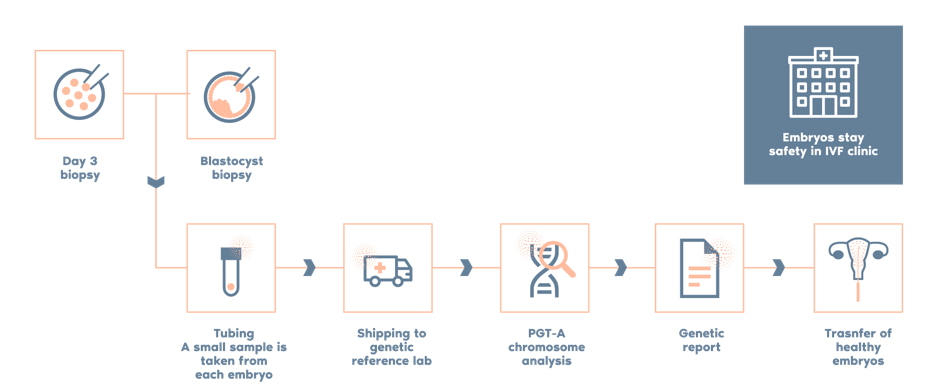
In couples with an abnormal SAT, it is clinically advisable to perform PGT-A (Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidies) to select chromosomally normal embryos for transfer.
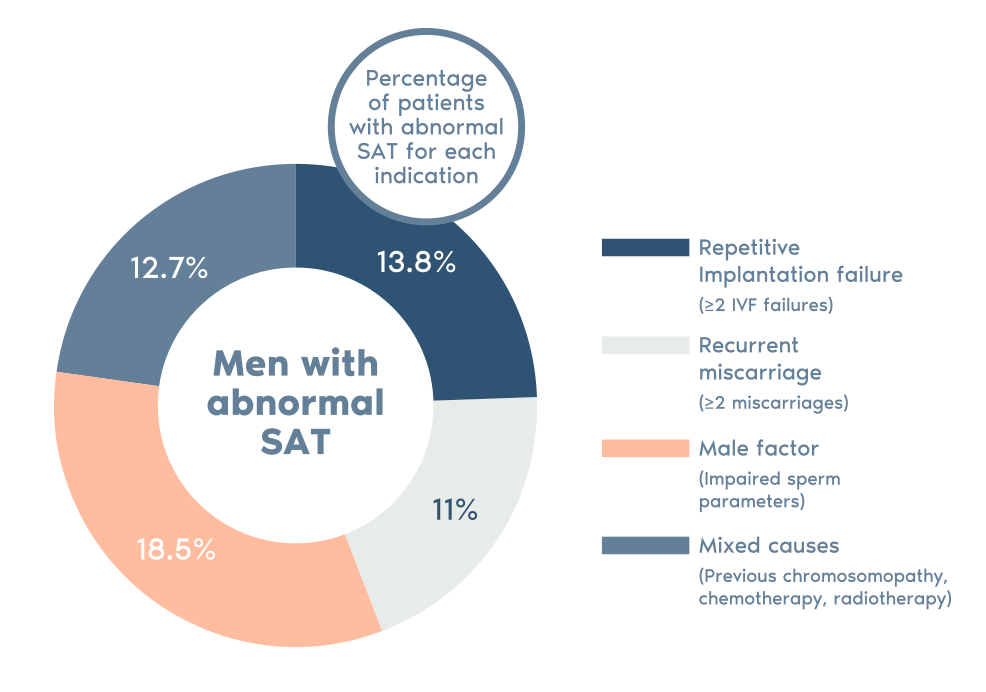
Is SAT for you?
This test is recommended if:
> You’ve suffered recurrent miscarriage
> You’ve had several IVF treatments without success
> You’ve had a previous pregnancy with chromosomal aneuploidy
> You’re a man with impaired sperm parameters