labneticspakistan.com
Llabnetics Pakistan
POC test on pregnancy remains
POC tests determine if a miscarriage was due to chromosomal abnormalities, offering options tailored to each patient’s needs.

A miscarriage
occurs In 25% of all
pregnancies
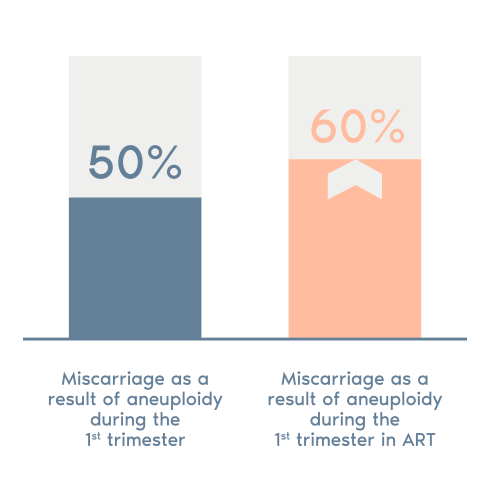
50% of miscarriages in the first term are due to chromosomal
abnormalities
This figure rises to 60% of pregnancies resulting from assisted reproduction

Informative results
of origen fetal en el foetal origin in 86.4% of cases
What is the POC test on pregnancy remains?
The family of POC tests analyse whether the miscarriage could have been caused by a
chromosomal abnormality.
> 50% of miscarriages in the first trimester present abnormalities in the number of chromosomes (aneuploidies).
> This figure rises to 60% in cases of assisted reproductive treatment and further increases with age.
> The POC test analyses the 24 chromosomes and can identify alterations to the number of chromosomes (aneuploidies) as well as losses and gains of chromosome fragments.
> Complementary analysis of STR (Short Tandem Repeats) microsatellite markers
in the patient’s blood enables us to identify ploidy alterations (haploid, triploid,
tetraploid) and determine the origin of the tissue under study (foetal or
maternal).
Why use the POC test on pregnancy remains?
There are three different tests that are adapted to the needs of each patient.
> Chromosomal analysis of fetal remains using POC testing is very useful for determining the possible cause of pregnancy loss and providing reproductive counseling to patients.
> Fetal origin results are obtained in more than 86% of cases.
> Identifies alterations in ploidy (haploid, triploid, tetraploid).
> Determines the maternal or fetal origin of the tissue analyzed.
> Can be performed on twin pregnancies.
Who is the POC test on pregnancy remains for?
> It is recommended for couples who have suffered a miscarriage, but it is essential for couples who have experienced recurring miscarriages or couples undergoing assisted reproductive treatment.
Limitations of the POC test on pregnancy remains
> This method does not detect balanced structural chromosomal abnormalities
and might not detect the following: aneuploidy in low-level mosaicism; triploids/tetraploids; uniparental disomy; and deletions or duplications inferior to 10 Mb.
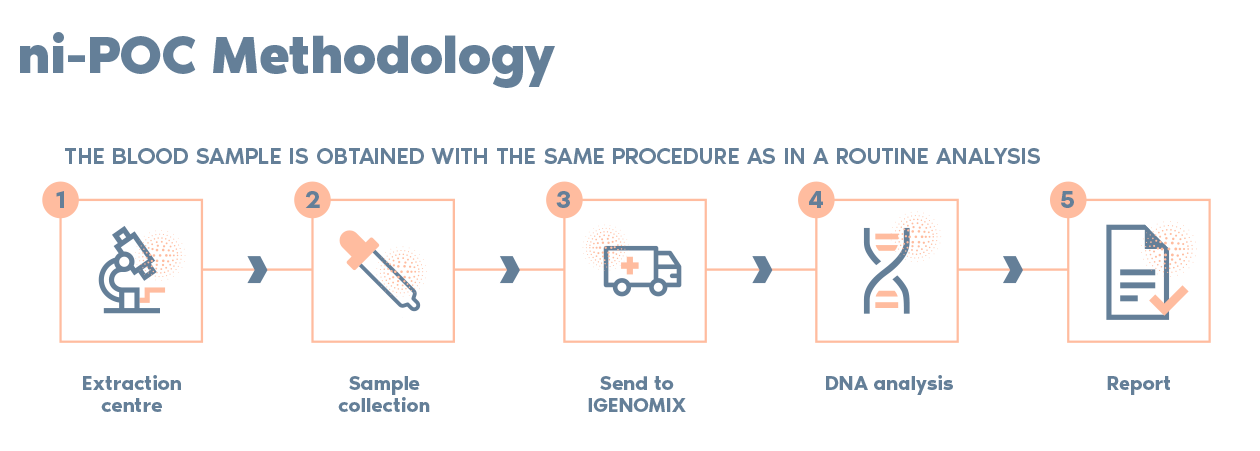
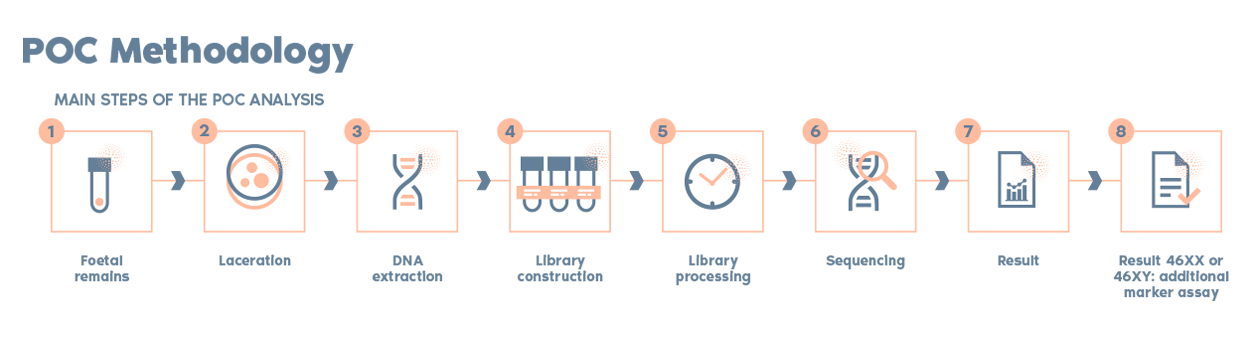
There are different methods depending on the test carried out: